Understanding the intricacies of pipe threading can be instrumental in ensuring the efficient operation of various fluid systems. Among the myriad of threading types, R and Rc threads, stemming from British Standards, are prominently utilized across multiple domains. Here’s a simplified insight into their differences, features, and application scenarios.
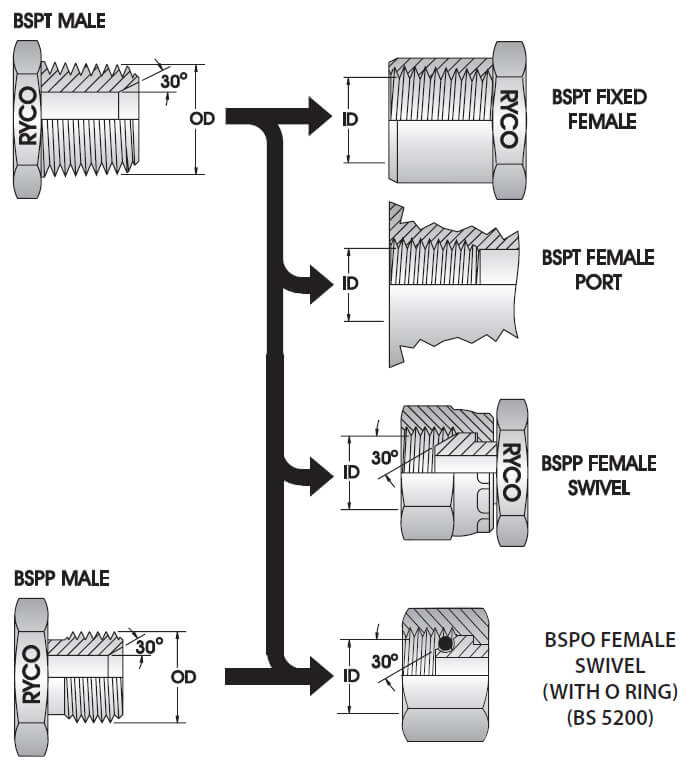
Image source from Ryco
A Look into R and Rc Threads:
R threads, synonymous with British Standard Pipe Taper (BSPT) threads, are external tapered threads designed for low-pressure liquid and gas transmission systems. They find broad applications in water and gas pipelines, air compression systems, and various industrial apparatus. Conversely, Rc threads, representing British Standard Pipe Taper Internal (BSPTI), are their internal counterparts, usually housed within pipe fittings to accept the external threaded connection from R threads.
The Difference:
- Thread Position: R threads are external, facilitating outer connections, whereas Rc threads are internal, designed to accept these external connections.
- Installation Compatibility: While R threads necessitate an external thread for pairing, Rc threads require an internal thread.
- Application Arena: R threads are a go-to for external pipeline connections like water or gas pipelines. In contrast, Rc threads are primarily used within pipe fittings, like flanges and sockets, to accept external thread connections.
Hallmarks:
- Tapered Design: Both threads sport a tapered design with an uneven pitch, aiding in a snug fit.
- Sealing Technique: Utilizing sealing paste or lubricant, both R and Rc threads ensure a robust seal, thwarting leaks effectively.
- Pressure Suitability: These threads are crafted for low-pressure systems, making them ill-suited for high-pressure applications.
Practical Utilization:
R Threads:
- Water Pipe Systems: Widely used for connecting water supply and drainage pipes, ensuring reliable, airtight connections.
- Gas Pipelines: Catering to gas and LPG pipelines, they meet the requisite safety standards.
- Air Compression Systems: Ideal for connecting compressors, cylinders, and other related apparatus, handling compressed air pressures proficiently.
- Industrial Equipment: Employed in connecting pipes and fittings in a plethora of industrial machinery like pumps and cooling systems.
Rc Threads:
- Pipe Fittings Interior: Primarily housed within pipe fittings to receive external threaded connections.
- Flange Connections: Commonly found in the internally threaded holes of flange connections, accepting externally threaded flange bolts and nuts.
Sealing Mechanism and Advantages:
Both R and Rc threads leverage sealing paste or lubricant to effectuate a sound seal, filling thread gaps efficiently. This sealing method not only prevents leaks but also facilitates easy maintenance and disassembly. The use of lubricant or sealant minimizes thread damage, making these threads a practical choice for numerous low-pressure applications.
In a nutshell, discerning the characteristics and applications of R and Rc threads can significantly bolster the efficiency and safety of fluid transmission systems across various industrial and domestic spheres.
Conclusion
R and Rc threads are different connection types, each with unique characteristics and applicability. Proper selection of the appropriate thread type is critical to ensuring a safe and reliable connection. By understanding the difference between R and Rc threads, we can better select the type of connection that suits our specific needs and ensure the safe and efficient operation of our piping system. Please feel free to contact us for more details.

